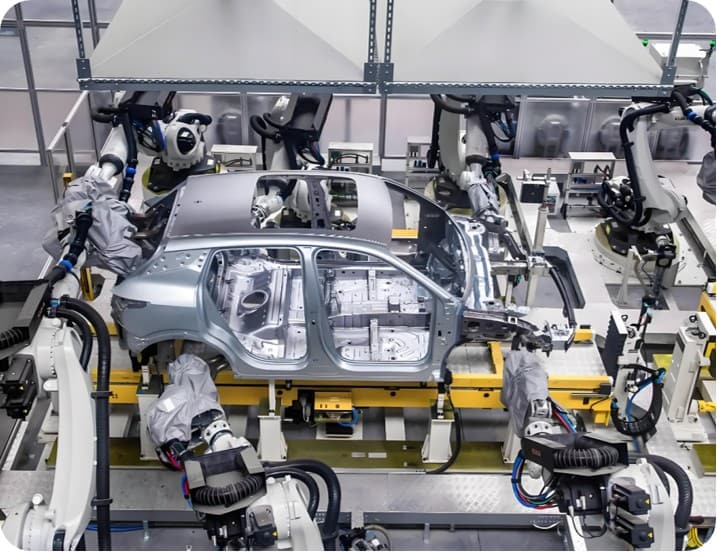
The BIW (Body in White) refers to the vehicle body that has been welded but not painted, including the welded assembly of vehicle body structural components and covering parts, and it is the core basic structure of automotive manufacturing.
The white body is the body assembly that has been welded in the process of automobile manufacturing but has not yet been painted. It is called Body in White in English.

It mainly includes:
Structural parts: such as longitudinal beams, transverse beams, columns, etc., determine the strength and safety of the body;
Cover: such as door, engine hood, fender, trunk lid, etc. (some definitions may exclude cover);
No interior or exterior trim, electronics or chassis systems installed.
The relationship with the vehicle:
After painting, the body is sequentially fitted with interior and exterior trim (such as seats and dashboards), electronic systems (such as wiring harnesses), chassis (such as suspension) and powertrain (such as engines), to form a complete vehicle.
The relationship with the vehicle After painting:
the body is sequentially fitted with interior and exterior trim (such as seats and dashboards), electronic systems (such as wiring harnesses), chassis (such as suspension) and powertrain (such as engines), to form a complete vehicle.

Manufacturing process characteristics:
Four core processes Stamping:
steel plate is made into parts through
stamping, drawing and other processes, and the utilization rate of materials should be optimized to reduce costs;
Welding: mainly spot welding, supplemented by laser welding and riveting (commonly used for aluminum alloy parts);
Painting: Electrocoating is one of the names of the white body;
Assembly: Completion of the integration of the body with other systems.

Design challenges
The strength and maintenance cost should be balanced (such as the integrated casting process may increase the cost of collision maintenance), and the error control should be optimized through 3D data.